本文最后更新于575 天前,其中的信息可能已经过时,如有错误请发送邮件到273925452@qq.com
文章目录[隐藏]

PWM不就做介绍了
PWM子系统驱动框架
PWM 子系统的主要组件包括 PWM 控制器驱动、PWM 设备模型和平台驱动。
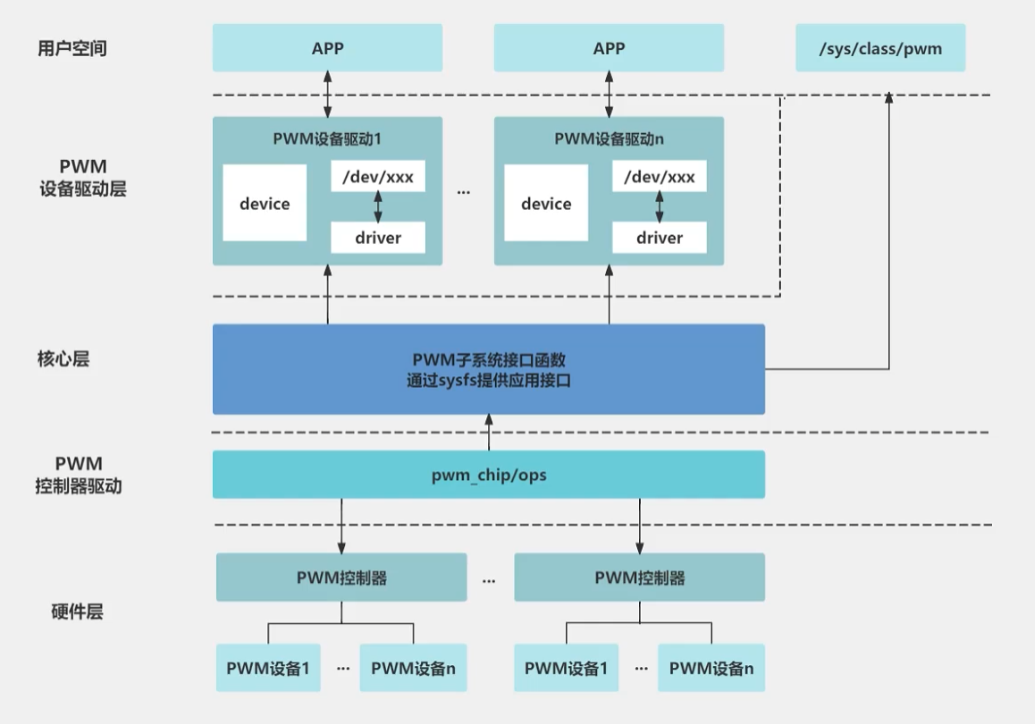
a. PWM 控制器驱动
PWM 控制器驱动是对实际 PWM 硬件的具体实现。它负责初始化硬件、配置 PWM 参数并控制 PWM 信号的输出。
b. PWM 设备模型
在 Linux 内核中,PWM 设备模型通过 pwmchip 和 pwm_device 结构体表示。pwmchip 代表 PWM 控制器,pwm_device 代表 PWM 通道。
c. 平台驱动
平台驱动用于将 PWM 控制器与硬件平台进行关联。它通过设备树(Device Tree)或平台数据(Platform Data)配置 PWM 控制器,并将 pwmchip 结构体注册到系统中。
Linux内核里的PWM驱动程序路径
/Linux-4.9.88/drivers/pwm
PWM子系统API接口
导出 PWM 通道:
- 函数: pwm_export()
- 作用: 使 PWM 通道在 /sys/class/pwm/ 中可用,以便用户空间应用访问。
- 用法:
int pwm_export(struct pwm_device *pwm, unsigned int flags);配置 PWM 参数:
- 函数: pwm_config()
- 作用: 配置 PWM 的周期(频率)和占空比(脉冲宽度)。
- 用法:
int pwm_config(struct pwm_device *pwm, unsigned int duty_ns, unsigned int period_ns);启动和停止 PWM:
- 函数: pwm_enable() 和 pwm_disable()
- 作用: 启动或停止 PWM 信号输出。
- 用法:
int pwm_enable(struct pwm_device *pwm);
int pwm_disable(struct pwm_device *pwm);获取 PWM 状态:
- 函数: pwm_get_state()
- 作用: 查询 PWM 当前的状态,包括周期和占空比。
- 用法:
int pwm_get_state(struct pwm_device *pwm, struct pwm_state *state);设置 PWM 信号的极性
- 函数:pwm_set_polarity()
- 作用: 设置 PWM 信号的极性(即信号的高电平和低电平的定义)
- 参数:PWM_POLARITY_NORMAL 或 PWM_POLARITY_INVERSED
- 用法:
int pwm_set_polarity(struct pwm_device *pwm, enum pwm_polarity polarity);从设备树中获取 PWM 设备的句柄
- 函数:devm_of_pwm_get()
- 作用: 从设备树中读取 PWM 设备的信息并获取 PWM 设备的句柄
- 参数
- dev: 设备结构体的指针。
- 用法:
struct pwm_device *devm_of_pwm_get(struct device *dev, const char *con_id);Code language: JavaScript (javascript)编写驱动框架
以sg90舵机为例
pwm_drv.c
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/poll.h>
#include "linux/jiffies.h"
#include <linux/delay.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/miscdevice.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/major.h>
#include <linux/mutex.h>
#include <linux/proc_fs.h>
#include <linux/seq_file.h>
#include <linux/stat.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/tty.h>
#include <linux/kmod.h>
#include <linux/gfp.h>
#include <linux/gpio/consumer.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include <linux/of_gpio.h>
#include <linux/of_irq.h>
#include <linux/interrupt.h>
#include <linux/irq.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/fcntl.h>
#include <linux/timer.h>
#include <linux/of.h>
#include <linux/gpio.h>
#include <linux/kthread.h>
#include <linux/pwm.h>
#include <linux/uaccess.h>
/* 主设备号 */
static int major = 0;
static struct class *sg90_class; // 设备类
static struct pwm_device *sg90_pwm_device; // PWM结构体操作指针
static ssize_t sg90_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file )
{
printk("====%s====\n", __FUNCTION__);
pwm_config(sg90_pwm_device, 500000, 20000000); // 设置PWM参数,初始角度,频率,单位ns
pwm_set_polarity(sg90_pwm_device, PWM_POLARITY_NORMAL); // 设置PWM极性
pwm_enable(sg90_pwm_device);
return 0;
}
static ssize_t sg90_read(struct file *file, char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset)
{
printk("====%s====\n", __FUNCTION__);
return 0;
}
static ssize_t sg90_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset)
{
int ret;
unsigned char data[1];
printk("====%s====\n", __FUNCTION__);
ret = copy_from_user(data, buf, size);
pwm_config(sg90_pwm_device, 500000+data[0] * 100000/9, 20000000);
return 0;
}
static int sg90_release(struct inode *node, struct file *filp)
{
printk("====%s====\n", __FUNCTION__);
pwm_config(sg90_pwm_device, 500000, 20000000);
pwm_free(sg90_pwm_device);
return 0;
}
/* 定义自己的file_operations结构体 */
static struct file_operations sg90_drv = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = sg90_open,
.read = sg90_read,
.write = sg90_write,
.release = sg90_release,
};
static int sg90_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
printk("====%s====\n", __FUNCTION__);
/* 注册file_operations */
major = register_chrdev(0, "sg90_chrdev", &sg90_drv); /* /dev/gpio_desc */
sg90_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "sg90_class");
device_create(sg90_class, NULL, MKDEV(major, 0), NULL, "sg90"); /* /dev/sg90 */
/* 从设备树获得硬件信息 */
sg90_pwm_device = devm_of_pwm_get(&pdev->dev, pdev->dev.of_node, NULL);
if (IS_ERR(sg90_pwm_device))
{
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "Failed to get PWM for sg90\n");
return PTR_ERR(sg90_pwm_device);
}
dev_info(&pdev->dev, "=======sg90 initialized successfully=====\n");
return 0;
}
static int sg90_remove(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
printk("======%s=======\n", __FUNCTION__);
device_destroy(sg90_class, MKDEV(major, 0));
class_destroy(sg90_class);
unregister_chrdev(major, "sg90_chrdev");
return 0;
}
/* 定义设备树匹配表,用于识别和支持特定的字符设备驱动器 */
static const struct of_device_id sg90_match_table[] = {
/* 匹配字符串 "fire,xxx" 用于标识 */
{.compatible = "fire,sg90"},
/* 空项作为匹配表的结束标志 */
{},
};
/* 定义platform_driver */
static struct platform_driver sg90_driver = {
/* 设置<驱动程序的名称>和<设备树匹配表> */
.driver = {
.name = "sg90", // 字符设备名
.of_match_table = sg90_match_table, // 设置设备树匹配表,用于设备的匹配
},
.probe = sg90_probe, // 设置探测函数,当设备被探测到时调用
.remove = sg90_remove, // 设置移除函数,当设备被移除时调用
};
/* 在入口函数 */
static int __init sg90_platform_driver_init(void)
{
int ret = 0;
printk("====%s====\n", __FUNCTION__);
ret = platform_driver_register(&sg90_driver); // 注册驱动程序
return ret;
}
/* 有入口函数就应该有出口函数:卸载驱动程序时,就会去调用这个出口函数
*/
static void __exit sg90_platform_driver_exit(void)
{
printk("====%s====\n", __FUNCTION__);
platform_driver_unregister(&sg90_driver); // 销毁设备信息
}
/* 7. 其他完善:提供设备信息,自动创建设备节点 */
module_init(sg90_platform_driver_init);
module_exit(sg90_platform_driver_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
Code language: HTML, XML (xml)了解 Heiweilu的小世界 的更多信息
订阅后即可通过电子邮件收到最新文章。









评论